Hypothesis Tree: A Simple Guide and Free PPT Template
Download our Hypothesis Tree guide and Powerpoint template using a computer:
Definition
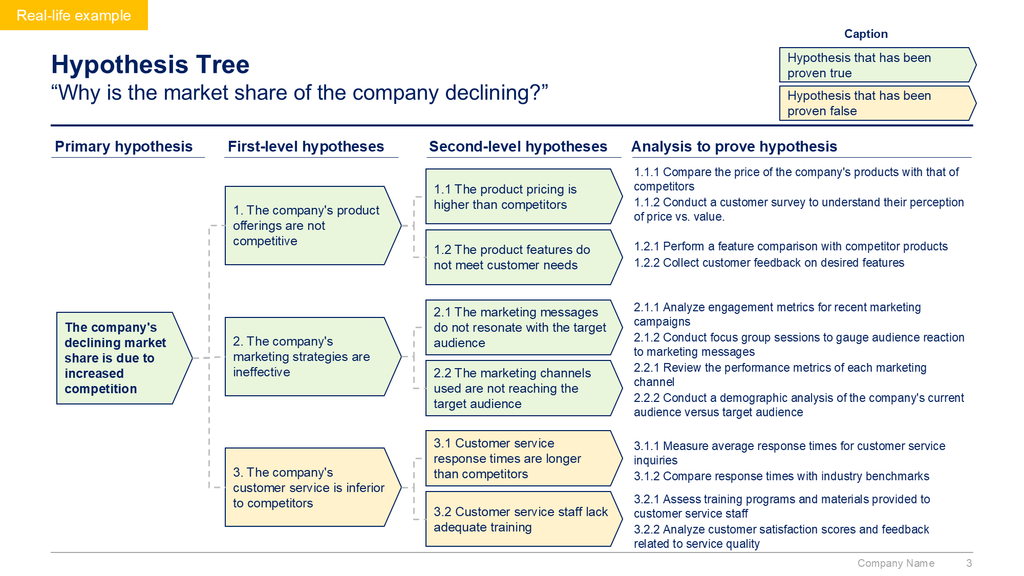
A Hypothesis Tree usually includes a primary question, and a hypothesis which is broken down into a set of sub-hypotheses. These sub-hypotheses should be mutually exclusive and collectively exhaustive (MECE), meaning they don't overlap and, when addressed together, comprehensively answer the primary question. Each sub-hypothesis is further disaggregated into more specific hypotheses, forming additional levels of branches, until the hypotheses are granular enough to be addressed through analysis.
Criteria for powerful hypothesis
Testable: It should be possible to prove or disprove the hypothesis through data analysis or research.
Open to debate: A good hypothesis should be neither obvious nor a simple statement of fact. It should provoke thought and discussion.
Significant impact: The hypothesis should be meaningful to the overall problem and have the potential to change the course of action if proven or disproven.
Actionable: The hypothesis should point to specific actions or interventions that the client can implement if the hypothesis is proven true.
Challenges
Premature conclusions: The hypothesis-driven approach can sometimes lead to premature conclusions, as teams may focus on proving their initial hypotheses instead of exploring alternative explanations or "outside the box" solutions.
Client perception: Clients may perceive the hypothesis-driven approach as arrogant or hasty, especially if they feel that the team has reached conclusions too quickly. It's essential to communicate the purpose of hypotheses and how they guide, rather than dictate, the analysis.
Advantages
Focus: By articulating the problem as a set of hypotheses, teams can target their analysis towards proving or disproving specific assumptions. This focus reduces wasted effort on irrelevant issues and helps prioritize the most impactful hypotheses.
Actionable insights: Hypothesis Trees inherently point to potential actions, as each hypothesis typically suggests a possible solution or intervention. By testing these hypotheses, teams can identify the most effective recommendations for their clients.
Iterative learning: Hypothesis Trees can be updated and refined as new information is gathered, allowing teams to adapt their analysis and recommendations based on emerging insights.
Need more help? Check our Toolkits:
- Corporate/Business Strategy and Strategic Planning Toolkit
- Financial Modeling, Planning & Analysis Toolkit


